Hello, everyone!
Today, I’d like to continue to share some knowledge about xPON networking protection.
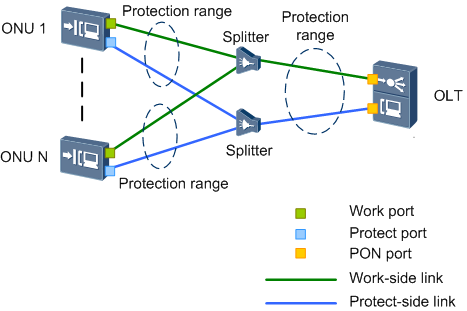
The xPON type C protection switching is implemented through the redundancy configuration of the two PON ports on the ONU, backbone optical fiber, optical splitter, and tributary optical fiber on an xPON network. Each item is in a dual configuration. The protection improves the reliability of the optical distribution network (ODN) and prevents service interruption.
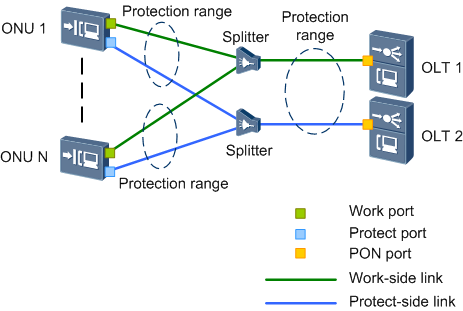
Type C provides redundancy for OLT (dual-homing), ONU’s PON ports, backbone fibers, optical splitters, and distribution optical fibers. When a fault occurs, services can be automatically switched to the functional link. After the fault is rectified, services are automatically switched back to the original link.
xPON type C protection can be deployed in two networking scenarios: single homing and dual-homing.
Figure 1 shows the xPON type C protection single homing network.
| Networking Mode | Advantage | Disadvantage | Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single homing | The networking mode is simple, and OLT and ONU can be managed easily. | When the OLT becomes faulty, services are interrupted. Optical fibers are deployed on the same channel and therefore two optical fibers may be broken at the same time. | This mode is used to protect important services, such as Enterprise private line services and base station services. |
Figure 2 shows the xPON type C protection dual-homing network.
Figure 2
| Networking Mode | Advantage | Disadvantage | Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dual homing | When the active OLT or its uplink fails, services can be switched to the standby OLT. | The networking mode is complicated and costly, and ONU management is difficult. | This mode is used to protect a power system or Enterprise private line services and base station services. |
Thank you for reading!
Any questions, please leave a message. csd@telecomate.com

Leave a comment