Introduction: XG-PON (10G Passive Optical Network) and XGS-PON (10G Symmetric Passive Optical Network) are both next-generation passive optical network technologies designed to deliver high-speed broadband services to end-users. While they share similarities in terms of performance and capabilities, there are also key differences between them. This article aims to explore and compare XG-PON and XGS-PON, shedding light on their unique features and applications.
XG-PON:
XG-PON, also known as 10G-PON, is an ITU-T standard that delivers symmetrical or asymmetrical data rates of up to 10 Gbps downstream and 2.5 Gbps upstream. It operates using time-division multiplexing (TDM) technology, where the downstream and upstream traffic are divided into different time slots to share the same fiber optic cable. XG-PON is widely deployed in Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) and Fiber-to-the-Building (FTTB) networks, offering high-speed internet access, IPTV, VoIP, and other broadband services to residential and business users.
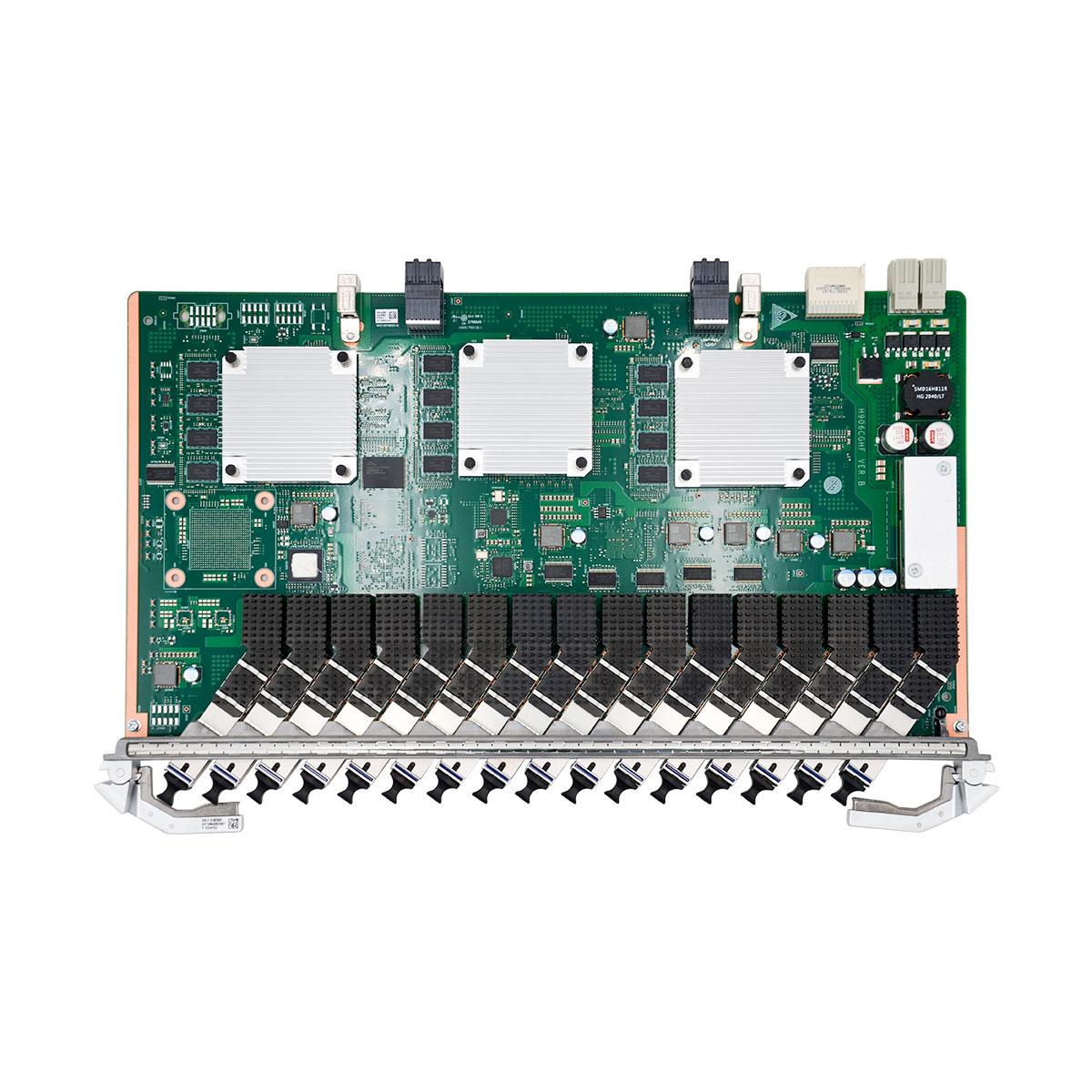
H906CGHF
Huawei MA5800 series 16-port XG-PON and GPON combo OLT Interface Board with XG-PON & GPON N2a Optical Module
XGS-PON:
XGS-PON, on the other hand, stands for 10G Symmetric Passive Optical Network. As the name suggests, XGS-PON provides symmetrical data rates of up to 10 Gbps downstream and upstream. Unlike XG-PON, XGS-PON utilizes wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology, enabling simultaneous transmission of downstream and upstream signals over the same fiber optic cable at different wavelengths. This allows for increased bandwidth efficiency and better support for symmetric services such as cloud computing, video conferencing, and real-time data backup.
H901CSHF
Huawei H901CSHF MA5800 series 16-port XGS-PON and GPON combo OLT interface board with XGS-PON & GPON B+/C+ optical module, apply to MA5800 series
Key Differences:
- Technology: XG-PON uses TDM technology, while XGS-PON employs WDM technology.
- Symmetry: XG-PON offers asymmetrical data rates, whereas XGS-PON provides symmetrical data rates.
- Bandwidth Efficiency: XGS-PON offers higher bandwidth efficiency due to simultaneous upstream and downstream transmission.
- Applications: XG-PON is suitable for applications where downstream traffic is dominant, such as internet browsing and video streaming, while XGS-PON is ideal for symmetric services and high-bandwidth applications requiring equal upstream and downstream speeds.
Conclusion:
In summary, both XG-PON and XGS-PON are advanced passive optical network technologies capable of delivering ultra-fast broadband services. While XG-PON is well-suited for traditional asymmetric applications, XGS-PON offers improved bandwidth efficiency and symmetric data rates, making it suitable for a wider range of applications, including cloud services, telecommuting, and multimedia content creation. Ultimately, the choice between XG-PON and XGS-PON depends on the specific requirements and use cases of the network deployment.
If you still have any questions, please feel free to contact: csd@telecomate.com.



Leave a comment