In a bustling Tokyo smart factory, autonomous robots glide across production lines while engineers in Osaka monitor real-time diagnostics through AR headsets. This seamless operation relies on two unsung heroes of networking: routers and access points (APs). Though often conflated, these devices play distinct yet complementary roles in our hyper-connected world. Understanding their differences isn’t just technical nitpicking—it’s the key to building robust, scalable networks for homes and enterprises alike.
The Network Traffic Directors
Routers: The Intelligent Gatekeepers
Modern routers have evolved into multifunctional command centers:
- IP Maestro: Assign unique addresses to every device, preventing data collisions
- Security Sentinel: Firewalls block 12,000+ intrusion attempts daily in average households
- Traffic Optimizer: QoS protocols prioritize video calls over file downloads
A typical Wi-Fi 6E router can manage 250+ connected devices, but its true brilliance lies in decision-making. When you stream a 4K movie, the router:
- Authenticates your device
- Negotiates bandwidth with your ISP
- Encrypts data via WPA3
- Dynamically switches frequencies to avoid interference
Access Points: The Signal Architects
APs specialize in blanket coverage without routing intelligence:
- Radio Frequency Engineers: Beamforming technology focuses signals like a laser pointer
- Seamless Roaming Enablers: 802.11k/v/r protocols hand off devices between APs mid-call
- Density Experts: Enterprise APs handle 100+ concurrent 4K streams
In a Seoul department store’s deployment, 47 APs created overlapping cells that maintained <1ms handoff latency for 10,000 daily shoppers’ devices.
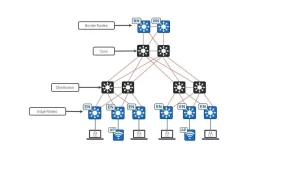
Enterprise-Grade Synergy
Retail Revolution
A California mall chain achieved 99.9% connectivity uptime by combining:
- Core Routers: Cisco Catalyst 9800 handling VLAN segmentation for stores/security/shoppers
- AP Array: Aruba 500 series APs providing location analytics via signal triangulation
- IoT Integration: Separate SSID for digital signage consuming 23TB monthly
Manufacturing Precision
An automotive plant’s network illustrates their分工:
- Routers: Isolate robotic arm control systems from office traffic
- APs: Enable AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle) coordination through warehouse dead zones
The Home Network Evolution
Modern mesh systems blur traditional boundaries:
- Hybrid Devices: Nest Wifi Pro functions as router + AP + smart speaker
- Self-Healing Networks: AI detects and bypasses failed nodes in 800ms
- Band Steering: Pushes 5GHz devices to less congested channels
However, purists argue dedicated AP/router combos deliver superior performance:
- Gaming Setup: ASUS ROG Rapture router + TP-Link Omada APs achieve 0% packet loss
- Smart Homes: UniFi Dream Machine + BeaconHD APs support 182 IoT devices
Future-Proofing Considerations
Wi-Fi 7 Realities
- Routers must handle 320MHz channels and 16 spatial streams
- APs require advanced heat dissipation for 30Gbps throughput
- Both need multi-gig Ethernet backhaul to avoid bottlenecks
Security Horizons
- Routers adopting post-quantum encryption standards
- APs integrating radar-based presence detection (no cameras)
Sustainability Demands
- Energy-efficient routers saving 800kWh annually per enterprise
- Solar-powered APs deployed in Amazonian research stations

Leave a comment