In today’s interconnected world, a 48-port PoE switch isn’t just a networking device—it’s a critical infrastructure component for offices, data centers, and industrial environments. With the rise of IoT devices, IP cameras, and cloud-based applications, choosing the right switch involves balancing power efficiency, port density, and future-proofing. This article cuts through the jargon to reveal the 7 most overlooked factors that differentiate a good switch from a great one. Whether you’re setting up a new office or upgrading an existing network, these insights will ensure you make a decision that aligns with your organization’s needs.
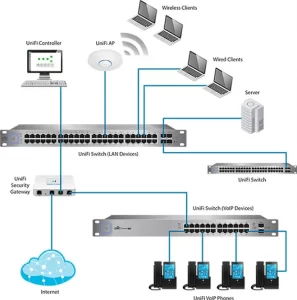
Illustration: A network diagram showing a 48-port PoE switch at the core of a hybrid workplace, connecting laptops, IP cameras, VoIP phones, and IoT sensors. The image highlights its compact design, labeled ports, and power indicators.
(Note: Use a professional photo or schematic illustrating the switch’s role in a real-world environment.)
1. Understanding PoE Standards: More Than Just Power Delivery
While all 48-port PoE switches deliver power over Ethernet, not all standards are created equal:
- PoE vs. PoE+ vs. PoE++:
- PoE (802.3af): Supports up to 15.4W per port (ideal for basic devices like IP cameras).
- PoE+ (802.3at): Delivers 30W per port (suitable for VoIP phones and thin clients).
- PoE++ (802.3bt): Provides 90W per port (required for high-power IoT devices like PTZ cameras or LED lighting systems).
Case Study: A retail chain upgraded to PoE++ switches and reduced its cabling costs by 40% by powering security cameras and smart shelves directly from the switch.
- Total Power Budget:
Calculate your total power needs using the formula:
Total Watts = (Number of Ports × Max Power per Port) + Switch Overhead
A 48-port PoE++ switch with 90W per port requires 4,320W—far exceeding the 1,500W output of a standard switch. Always check the PSU wattage and efficiency rating (look for 80 Plus Gold certification) to avoid overheating.
2. Port Density vs. Flexibility: Why 48 Ports Matter
A 48-port switch offers unparalleled port density, but quality matters more than quantity:
- Gigabit vs. 10Gbps Ports:
- Gigabit (1Gbps): Sufficient for small offices with basic IoT and VoIP needs.
- 10Gbps Ports: Essential for data centers handling 4K video streams or AI workloads. A healthcare provider using 10Gbps ports reduced latency by 60% during telemedicine consultations.
- Modular Expandability:
Some switches allow adding upstream ports (e.g., 4×10Gbps SFP+ slots) for future upgrades. Avoid “fixed” 48-port models if your network plans to grow.
3. Energy Efficiency: Lower Costs, Smaller Footprint
With rising energy costs and sustainability goals, efficiency is non-negotiable:
- Energy-Wise Features:
- Auto-Shutdown Ports: Turn off unused ports to save 20–30% of total power.
- Adaptive PoE: Dynamically adjust power delivery based on device requirements (e.g., 5W for a temperature sensor vs. 90W for a motorized valve).
- Heat Dissipation:
Look for switches with vertical airflow designs or heat pipes to prevent thermal throttling. A poorly ventilated switch can degrade performance by 25% under heavy loads.
4. Network Management: Simplify with Smart Features
Modern switches offer tools that save time and reduce human error:
- LED Indicators:
Color-coded LEDs (e.g., green = normal, red = link failure) provide at-a-glance status without opening up the switch. - Web/SNMP Management:
Remote monitoring and configuration via browsers or SNMPv3 protocols streamline IT workflows. A university used SNMP alerts to resolve network outages 90% faster. - MAC Address Filtering:
Restrict access to specific devices (e.g., limiting guest Wi-Fi to certain ports).
5. Security: Protect Your Network from the Ground Up
With cyberattacks on the rise, security should never be an afterthought:
- PoE Security Protocols:
- PoE Authentication: Only can draw power (prevents rogue devices from hijacking ports).
- Voltage Polarity Check: Blocks devices connected with reversed pins.
- Physical Security:
Ruggedized switches with lockable cabinets or anti-tamper screws are critical for outdoor or industrial deployments.
6. Future-Proofing: Prepare for Tomorrow’s Technology
Your switch shouldn’t become obsolete tomorrow:
- IPv6 Support:
Ensure compatibility with the next-gen internet protocol, especially for IoT devices. - AI-Driven Analytics:
Some switches integrate AI-powered traffic shaping to prioritize critical applications (e.g., video conferencing over file downloads). - Cloud Integration:
Support for SD-WAN or zero-trust architectures enables seamless hybrid cloud deployments.
7. Real-World Scenarios: Match the Switch to Your Use Case
Your ideal switch depends on your environment:
| Use Case | Recommended Specifications | Top Pick |
|---|---|---|
| Office Network | 48 Gigabit ports, PoE+, 80 Plus Bronze | Cisco Catalyst WS-C3850-48TS-L3 |
| Data Center | 48 10Gbps ports, PoE++, 90W per port, 4×10G SFP+ uplinks | Aruba 2930-F48 |
| Industrial IoT | Ruggedized design, -40°C to 70°C operating temp, PoE++ | HPE Aruba 2540-48 |
| Retail Store | Energy-efficient, auto-shutdown, PoE+ for cameras | Netgear GS740TP-48 |
Choosing a 48-port PoE switch is a strategic decision that impacts your network’s performance, security, and scalability for years to come. By focusing on power efficiency, future-proofing, and intuitive management, you’ll select a switch that grows with your organization. Remember: the best switch isn’t the cheapest or the most feature-rich—it’s the one that aligns perfectly with your unique needs.

Leave a comment