Issue Description
Handling Process
1. Login the access switch “xx-xx-xx-1” xx.xx.xx.xx, and found the member interface XG0/0/4 of eth-trunk 1 with high usage (100%) of bandwidth:
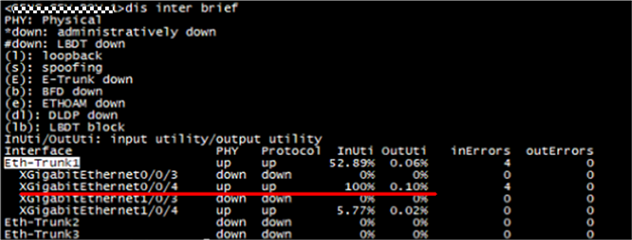
2. “Display interface XGigabitEthernet 0/0/4” to find a lot of broadcast packets enter XG0/0/4 of eth-trunk1 on access switch “xx-xx-xx-1”. Then make capture by command “capture packet interface xxx” to know the VLAN of broadcast packets is 26.
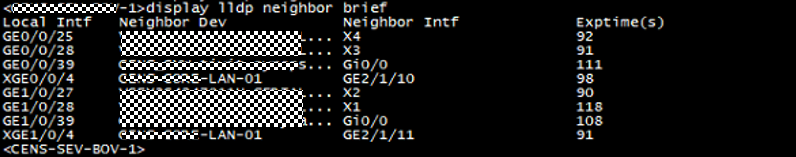
3. Check the LLDP neighbor of member interfaces of eth-trunk1, to know the peer device is Core switch “xxxx-xxxx-LAN-01”:
4. Login the core switch “xxxx-xxxx-LAN-01”, found the MAC-flapping on the VLAN26 and produced a large number of broadcast packets, which flooded to the access switch “xx-xx-xx-1” via interface eth-trunk3:

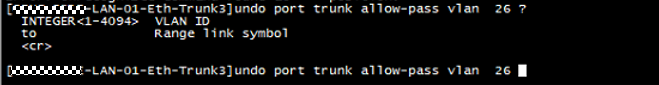
5. Reviewed configuration with customer and confirmed that traffic of VLAN26 is not necessary for the access switch “xx-xx-xx-1”, then remove the VLAN 26 under eth-trunk3 on the core switch “xxxx-xxxx-LAN-01”, then the usage of eth-trunk1 return to normal value on the access switch “xx-xx-xx-1”:
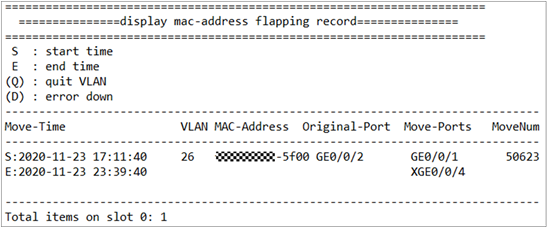
6. Check the loop of VLAN26, “Display lldp neighbor brief” and “Display mac-address flapping record” to find the issue switch “xx-xx-xx-LAN-S03”, its GE0/0/1 and GE0/0/2 was connected directly with loop.
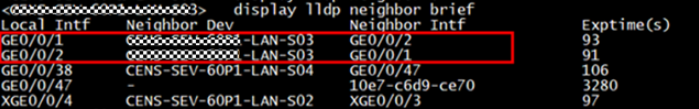
7. Then apply the customer’s approval and shutdown GE0/0/1 to destroy the loop.
Root Cause
Solution
Final solution: Shutdown the interface GE0/0/1 to destroy the loop on the issue switch “xx-xx-xx-LAN-S03”, then the MAC-flapping and abnormal broadcast packets stopped.

Leave a comment