
Networking:
As shown in Figure 4-2, OSPF is configured on SwitchA, SwitchB, SwitchC, and SwitchD, and router IDs and IP addresses have been configured for the devices.
Figure 4-2 IP address conflict on a network:
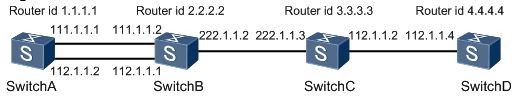
Route Flapping Caused by an IP Address Conflict.
Alarm Information
The following problems may occur due to IP address conflicts between interfaces on different devices:
- The CPU usage is high. You can run the display cpu-usage command to check the CPU usage. The command output shows that the ROUT task consumes much more CPU resources than other tasks.
- Route flapping occurs.
Handling Process
- Run the display ospf lsdb command on each switch once per second to check information about the OSPF link state database (LSDB) on the switches.
- Collect the command output on each switch. Locate the fault based on the collected information.
- Scenario 1
The aging time (Age field) of a network LSA is 3600 on a switch or the switch does not have the network LSA, and the Sequence value increases quickly.
On the other switches, the aging time of the same network LSA frequently alternates between 3600 and smaller values, and the Sequence value increases quickly.
If the preceding conditions are met, LSA aging is abnormal.
The following provides a command output example:
<HUAWEI> display ospf lsdb
OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 3.3.3.3
Link State Database
Area: 0.0.0.0
Type LinkState ID AdvRouter Age Len Sequence Metric
Router 4.4.4.4 4.4.4.4 2 48 8000000D 1
Router 3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 6 72 80000016 1
Router 2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 228 60 8000000D 1
Router 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 258 60 80000009 1
Network 112.1.1.4 4.4.4.4 121 32 80000001 0
Network 112.1.1.2 1.1.1.1 3600 32 80000015 0
Network 222.1.1.3 3.3.3.3 227 32 80000003 0
Network 111.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 259 32 80000002 0
AS External Database
Type LinkState ID AdvRouter Age Len Sequence Metric
External 33.33.33.33 4.4.4.4 206 36 800001D7 1
External 125.12.1.2 4.4.4.4 206 36 80000032 1
Run the display ospf routing command on each switch once every second. If route flapping occurs but the OSPF neighbor relationship does not flap, IP address conflicts or router ID conflicts have occurred. Based on the display ospf lsdb command output, it is determined that the IP address of the designated router (DR) conflicts with that of a non-DR.
Locate one switch that uses the conflicting IP address based on the AdvRouter value and then find the conflicting interface on the switch. The other switch is difficult to find based only on OSPF information. You need to check interface IP addresses against the IP address plan to locate this switch.
In this example, first determine that the conflicting IP address is 112.1.1.2, and the router ID of a conflicting device is 1.1.1.1. However, the other conflicting device (3.3.3.3) cannot be located based on OSPF information.
- Scenario 2
If the LinkState ID values of two network LSAs are both 112.1.1.2 on a switch, the aging time of the two network LSAs is short, and the Sequence value increases quickly, then an IP address conflict has occurred between the DR and BDR.
<HUAWEI> display ospf lsdb
OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 3.3.3.3
Link State Database
Area: 0.0.0.0
Type LinkState ID AdvRouter Age Len Sequence Metric
Router 4.4.4.4 4.4.4.4 17 48 8000011D 1
Router 3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 21 72 8000015A 1
Router 2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 151 60 80000089 1
Router 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 1180 60 8000002A 1
Network 112.1.1.2 3.3.3.3 3 32 8000016A 0
Network 112.1.1.2 1.1.1.1 5 32 80000179 0
Network 222.1.1.3 3.3.3.3 145 32 8000002D 0
Network 212.1.1.4 4.4.4.4 10 32 80000005 0
Network 111.1.1.2 2.2.2.2 459 32 80000003 0
AS External Database
Type LinkState ID AdvRouter Age Len Sequence Metric
External 33.33.33.33 4.4.4.4 30 36 800001DC 1
External 125.12.1.2 4.4.4.4 30 36 80000037 1
Change the IP address of a conflicting device based on the IP address plan.
Root Cause
On an OSPF network, IP address conflicts between interfaces may cause frequent aging and generation of link-state advertisements (LSAs), which results in network instability, route flapping, and high CPU usage.
Suggestions
On an OSPF network, IP address conflicts between interfaces may cause frequent aging and generation of LSAs, which results in network instability, route flapping, and high CPU usage.
Therefore, configure IP addresses for interfaces according to the plan, and do not modify planned network parameters. If an IP address conflict occurs, locate the conflicting devices and rectify the fault in a timely manner.

Leave a comment