By now, PPPoE and IPoE are widely used in the terminal accessing scenario. Though both of them are used to authenticate the access users, there is much difference between PPPoE and IPoE. We’ll talk about the difference in this post.
Generally, we access the internet through the PPPoE dialer, in which way, the modem gets an IP address from the ISP. Besides this way, some users may notice that they don’t need to fill in a username and password and can get to the internet directly. Actually, in this situation, they may be under a DHCP service.
Nowadays, Most ONTs on the market support PPPoE, IPoE, and DHCP, whether they are Huawei, ZTE, Fiberhome, or third-party M329, M520, or M454.
What is PPPoE?
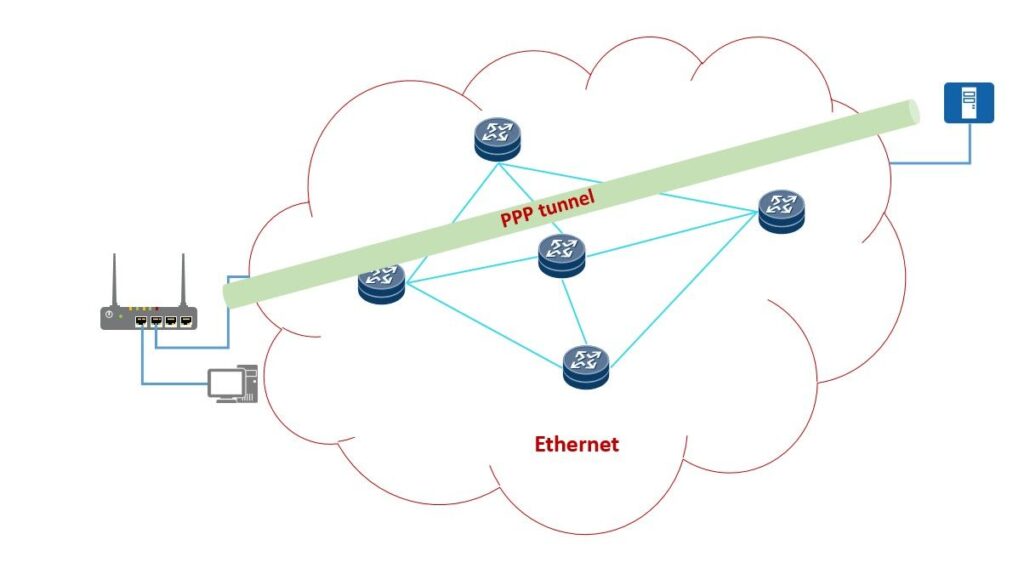
PPPoE(PPP over Ethernet) is a technology that establishes a PPP connection over the ethernet. As known, ethernet doesn’t support authenticating access users, while PPP does, but PPP is a point-to-point protocol, it requires a point-to-point link, and it will cost a lot of money to establish a point-to-point link between ISP and users. Think about the physical links between users and ISP in your city.
To eliminate the disadvantages of both PPPoE and IPoE, the PPPoE is introduced.
PPPoE allows multi-logical PPP links established over the ethernet, and it’s widely used when dialer users access the Internet.
PPPoE authentication mechanism brings not only security but also complexity.
With the spreading of IPTV, PPPoE is not suitable in these situations. Since PPPoE requires the dialer terminal, these devices are not able to install such software. Also, since the PPPoE is a virtual PPP link between ISP and dialer users, the BRAS, which dialer users access, would become the bottleneck when spreading multicast traffic.
In these scenarios, the IPoE could be the best choice.
What is IPoE?
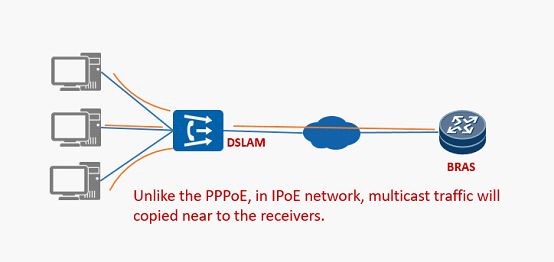
In IP over Ethernet (IPoE) scenario, a PC is connected to the Ethernet interface of a BRAS through a Layer 2 device (such as LAN Switch). When the PC accesses the IPv4 network, a user IP packet is encapsulated into an IPoE packet on the Ethernet interface. The IPoE packet is forwarded to the BRAS through the Layer 2 device. The BRAS then authenticates the user and authorizes user services based on physical or logical information carried in the IP packet, such as the MAC address, VLAN ID, and Option 82 (line information).
Unlike the PPPoE, IPoE is easy to use and does not need any client dial-in software. IPoE authenticates and charges users based on their physical location (identified by a unique VLAN ID / PVC ID). Users do not need to enter a username and password when they access the Internet.
What is DHCP?
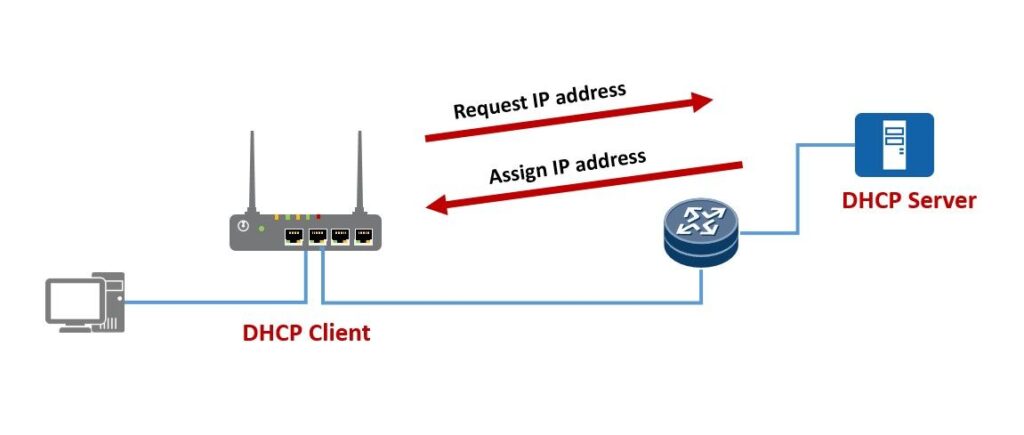
DHCP, also called Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, is a network management protocol for dynamic and centralized IP address allocation and management. It was first defined in October 1993 based on BOOTP. As defined in RFC 2131, DHCP operates based on the client-server model. A DHCP client applies to a DHCP server for network parameters, such as the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway address, and DNS server address. The DHCP server then replies with the configuration parameters to the client so the client can communicate with other IP networks.
The same as the Ethernet, it’s impossible to authenticate DHCP users. So far DHCP accessing is usually used in a campus network, in which the access user has been authorized before.


Leave a comment