
The EoS boards include the interface boards and processing boards for FE and GE services. Today I will introduce you to the EAS2 board, describes the version, application, functions, front panel, and technical specifications of the EAS2 (2-port 10xGE switching and processing board). This article will also tell you the difference between N1EAS2 and N3EAS2.
- Front Panel differences
The EAS2 is available in the following functional versions: N1 and N3.
From the front panel images, N1 and N3 version have some differences:

N1EAS2 Front Panel
N3EAS2 Front Panel
- Version mapping difference of N1EAS2 and N3EAS2
N1EAS2 start version: V100R008C01
N3EAS2 start version: V200R012C01
The N3EAS2 and N1EAS2 interconnect with other devices using the GFP encapsulation.
If the FCS parameter at the remote end is different from that at the local end, the N1EAS2 supports self-adaptation and there is no need to manually set the FCS parameter to the same value. The FCS_ERR alarm is not reported.
The N3EAS2 does not support self-adaptation. Therefore, an FCS_ERR alarm will be reported and you need to manually set the FCS parameter to the same value.
- Application
The EAS2 is used to transmit/receive Ethernet services, manage bandwidths, and realize Layer 2 switching of Ethernet services.
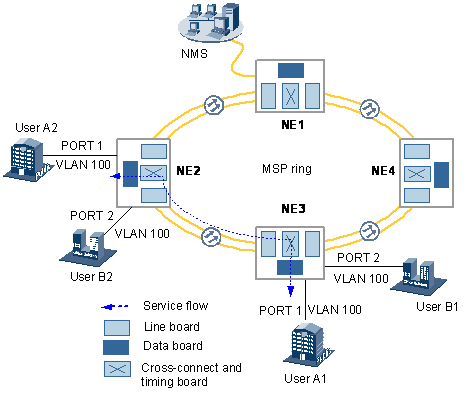
- Functions and Features
EAS2 boards support the transmission of 10 GE Ethernet services, LCAS, and test frame functions.
- The differences of valid slots between N1 and N3 version
N1EAS2: An N1EAS2 board can be installed in any of slots 5-8 and 11-14 in a subrack and provides a bandwidth of 10 Gbit/s.
N3EAS2: An N3EAS2 board can also be installed in any of slots 5-8 and 11-14 in a subrack. When an N3EAS2 board is installed in slot 5, 6, 13, or 14, it provides a bandwidth of 10 Gbit/s; when an N3EAS2 board is installed in slot 7, 8, 11, or 12, it provides a bandwidth of 20 Gbit/s.
- The differences of pluggable optical modulebetween N1 and N3 version
XFP optical modules supported on N1EAS2 boards.
SFP+ optical modules supported on N3EAS2 boards.
N3EAS2 supports one-fiber bidirectional optical modules.
- The differences of Ethernet virtual private line (EVPL) servicebetween N1 and N3 version
Supports PORT-shared EVPL services.
Supports VCTRUNK-shared EVPL services.
The services are isolated by VLAN tags.
The services are isolated by MPLS tags (supported on N3EAS2 boards).
The services are isolated by QinQ tags.
Supports a maximum of 2048 links in the case of the N1EAS2; supports a maximum of 4096 links in the case of the N3EAS2.
- The differences of MPLS technologybetween N1 and N3 version
Not supported on N1EAS2 boards
Tunnel-based EVPL (transit) supported on N3EAS2 boards
- The differences of maximum bound bandwidthbetween N1 and N3 version
N1EAS2: 64xVC-4 or 192xVC-3
N3EAS2: 128xVC-4
- The differences of VCTRUNK specificationsbetween N1 and N3 version
An N1EAS2 board supports a maximum of 24 VCTRUNKs.
The maximum number of VCTRUNKs supported by the N3EAS2 board is as follows:
If the slot bandwidth is 10 Gbit/s, the maximum number is 17 (VCTRUNK1 to VCTRUNK17).
If the slot bandwidth is 20 Gbit/s, the maximum number is 34 (VCTRUNK1 to VCTRUNK34).
- Protection schemes
MSTP:
Not supported on N1EAS2 boards
Supported on N3EAS2 boards
ERPS:
Not supported on N1EAS2 boards
Supported on N3EAS2 boards
From the above article, we can see some functions of EAS2, and the differences between N1EAS2 and N3EAS2.
At present, the number of EAS2 in the market is relatively small. If you are interested in this board, please contact csd@telecomate.com.

Leave a comment