Hello everyone,
Switches, as one of the important components of the network, are classified into manageable switches and non-manageable switches according to the management type. So, what is the difference between a non-manageable switch and a manageable switch? Today we will talk about this topic.
Unmanaged Switches
The non-Manageable switch is a network switching device that works on the second layer (data link layer) of the OSI network reference model. The data forwarding of the Non-Manageable switch is based on the MAC address, it can identify the MAC address in the data packet, and send the data to the corresponding port according to the MAC address table stored inside it. In the initial state, when the MAC address table is empty, the switch will broadcast data to all ports. As data is sent and received, the switch gradually establishes the relationship between the MAC address and the port and updates it in time according to the actual situation.
Advantage
1. Flexible use, plug and play.
2. The price is cheap, saving money.
3. Large number of ports.
Disadvantage
1. Non-manageable switches have limited functions, suitable for small networks, and have major limitations on network upgrades/expansion.
2. Does not support ARP protection, MAC address binding, and VLAN division. It is prone to broadcast storms, flooding, etc., which can lead to network paralysis.
3. Does not support flow control.
4. The reliability of data transmission is poor, and packet loss is serious.
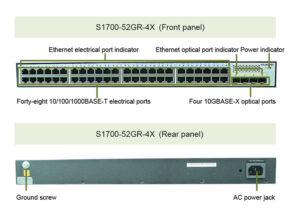
The picture below shows Huawei’s non-manageable switch S1700-52GR-4X:
Managed Switches
The Manageable switch works on the third layer (network layer) of the OSI network reference model, supports VLAN division, supports routing functions, supports SNMP protocol (Simple Network Management Protocol), and can be configured through the web.
Advantage
1. The networking is flexible and applies to large and medium-sized networks. The port is flexible, and different interface types can be selected according to the application of the network: such as SFP, GE, etc.
2. It has good security performance, supports ARP protection, MAC address binding, and VLAN division.
3. Support QoS, flow control, port mirroring, and can filter, shape, and supervise the flow.
4. The manageable switch has good performance. The backplane has large bandwidth, fast data forwarding speed, low packet loss rate, and low latency.
5. Support SNMP, Web, Telnet, SSH functions, which can be managed through network management software, and can also be accessed remotely to increase network security and controllability.
Disadvantage
1. Higher price than non-manageable switches.
2. Compared with non-manageable switches, the operation is more complicated and requires configuration.
The picture below shows Huawei’s manageable switch S5731-S24T4X:

Summarize
The manageable switch has strong functions and good stability, and is suitable for large-scale network environments; the non-manageable switch, plug and play, is relatively cheap and is widely used in the establishment of small networks. Sometimes these two types of switches can be used in combination, and some remote devices can be mounted on non-manageable switches and unified feedback to the manageable switches.
That is all I want to share with you!

Leave a comment