What is BRAS?
BRAS, which is called Broadband Remote Access Server, is a new type of access gateway for broadband network applications. It is the bridge between the backbone of broadband access network, providing basic access means and management functions of broadband access network. It is located at the edge of the network, providing broadband access services, realizing convergence and forwarding of multiple services, and meeting the requirements of different users for transmission capacity and bandwidth utilization, so it is the core equipment for broadband user access.

Broadband-Remote-Access-Server
Before we introduce BRAS in detail, let’s start with the general relationship between networks to facilitate a more in-depth understanding. The transport network is the base of our entire communication network, responsible for connecting home users, government and enterprise users and data centers everywhere. It is also the backbone of the Internet. The entire transmission network, respectively, is the backbone network and the metropolitan network. The backbone network is further divided into national backbone network and provincial backbone network. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is the communication network within a single city (abbreviated as MAN, Metropolitan Area Network). MAN is also further subdivided into three layers: core layer, convergence layer and access layer.
Nowadays, we all have fiber optic Internet access, and every household has ONT (Optical Network Terminal). ONT belong to PON (Passive Optical Network) system. PON system belongs to the access layer of metro network, and PON, to be frank, is to turn one fiber into uncountable fiber to realize the “optical connection” of thousands of households. You may think of routers. Router is also the role of distribution and aggregation, a network cable into uncountable network cables.
PON is the bottom system, it is only responsible for light, only responsible for delivering light to your home. In other words, it just connects the water pipe to your house, but there is no water in the pipe. To have water, you must first go to the water company to open an account. Without BRAS, the operator cannot identify the user, determine the user’s authority, or bill the user.
After all, where exactly is BRAS? As shown in the figure below, BRAS is generally deployed in the core layer of MAN. Nowadays, the popular layering method will also call the layer where BRAS is located as service control layer.
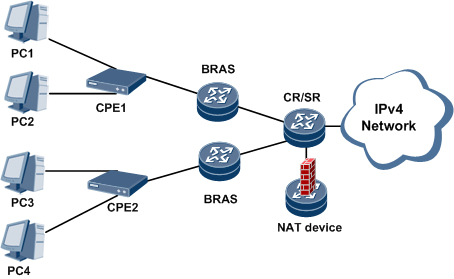
BRAS is the bridge between the access network and the backbone network. It is a gateway that firmly controls the user’s data in and out of the backbone network. the BRAS performs authentication and billing functions by cooperating with the authentication system and billing system. In other words, it is like a toll booth of the highway, managing and billing users. It is further up the core router CR of the backbone network, which is the entrance and exit of the whole MAN traffic.
- CR: Core Router
- SR: Service Router
- SW: Switch
The most common switch models on the market today are: Huawei S5700 series, S7700/S9700 series.
If users want to access the Internet, they must first make sure that the optical path of the PON is OK. Then, between the optical cat (which can also be a wireless router) and the BRAS, a PPP session is established.
* PPP, Point to Point Protocol, is a data link layer protocol.
Once a PPP session is established, users can access the Internet. The PPPOE we talked about earlier is PPP over Ethernet (there was also PPPOA, or PPP over ATM).
It is worth mentioning that as the performance of the device improves, the positioning of BRAS has changed a bit in addition to the change in form. The BRAS and SR (Service Router) that we saw together earlier, the device functions are gradually converging into MSE (Multi-Service Edge) or BNG (Broadband Network Gateway). This is also some form of amalgamation.
Thanks for reading. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact: csd@telecomate.com.

Leave a comment