In an age where milliseconds can determine market success and cyber threats lurk in every packet, enterprises can no longer afford the limitations of traditional networking hardware. Enter Layer 3 switches—a hybrid marvel that combines the speed of Layer 2 switching with the intelligence of routing. These devices are quietly transforming networks from static pipelines into dynamic, self-optimizing ecosystems. For IT leaders balancing performance, security, and scalability, Layer 3 switches aren’t just an upgrade—they’re a strategic imperative.
The Evolution: From Layer 2 to Layer 3
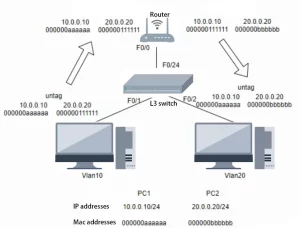
Layer 2 switches, the workhorses of early networking, operate by forwarding data frames based on MAC addresses. While efficient for simple LAN segmentation, they lack the ability to route traffic between subnets or prioritize data based on application needs. Layer 3 switches bridge this gap by integrating routing capabilities directly into the switching hardware, enabling:
- Inter-VLAN Routing: Direct communication between different VLANs without a standalone router.
- IP-Based Decision Making: Forwarding traffic using IP addresses for granular control.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Prioritizing critical traffic like VoIP or video conferencing.
A hospital network, for instance, might use a Layer 3 switch to isolate MRI machine traffic (VLAN 10) from patient records (VLAN 20) while allowing secure communication between them—a task requiring both switching speed and routing logic.
Performance Unleashed: Speed Meets Intelligence
1. Hardware-Based Routing
Unlike software-based routers that introduce latency through CPU processing, Layer 3 switches use Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) to route traffic at wire speed. For a financial trading firm in Chicago, deploying Cisco Catalyst 9300 switches reduced order execution latency from 800µs to 50µs—translating to millions in daily arbitrage gains.
2. Scalability Without Complexity
Layer 3 switches support hierarchical addressing and dynamic routing protocols like OSPF and BGP. This allows enterprises to scale networks without manual reconfiguration. A global e-commerce platform automated warehouse network expansions using Aruba 8320 switches, cutting deployment times from weeks to hours.
3. Bandwidth Optimization
By implementing Equal-Cost Multi-Path (ECMP) routing, Layer 3 switches distribute traffic across multiple paths, preventing bottlenecks. A video streaming provider eliminated buffering during peak hours by balancing loads across 10G links using Juniper EX4300 switches.
Security: From Reactive to Proactive
Layer 3 switches embed security features that traditional Layer 2 devices can’t match:
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): Blocking unauthorized IP addresses or protocols at the switch port level.
- DHCP Snooping: Preventing rogue DHCP servers from hijacking IP assignments.
- Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI): Stopping ARP spoofing attacks in real time.
In 2023, a European university thwarted a ransomware attack targeting its IoT-enabled campus by using Extreme Networks’ Layer 3 switches to quarantine infected smart lighting systems within milliseconds.
Cost Efficiency: Consolidating Hardware and Overhead
Deploying separate routers and switches inflates costs through power consumption, rack space, and management overhead. Layer 3 switches consolidate these functions:
- A manufacturing plant saved $120,000 annually by replacing 8 legacy routers with two HPE 5900AF switches.
- Integrated Power over Ethernet (PoE++) in models like the Ubiquiti USW-Pro-48-PoE powers devices like IP cameras and access points, eliminating external power supplies.
Use Cases: Where Layer 3 Switches Shine
1. Campus Networks
Universities and corporate campuses use Layer 3 switches to segment departments (HR, R&D) into secure VLANs while enabling cross-department collaboration via inter-VLAN routing.
2. Data Centers
High-density environments leverage Layer 3 switches for spine-leaf architectures, reducing east-west traffic latency between servers.
3. IoT and Edge Computing
Smart cities deploy ruggedized Layer 3 switches (e.g., Cisco IE3400) to locally process traffic from thousands of sensors, reducing cloud dependency.
The Future: SDN and AI Integration
Modern Layer 3 switches are evolving into programmable platforms. With support for Software-Defined Networking (SDN), switches like Arista 7050X3 enable network automation via APIs. Meanwhile, AI-driven models predict traffic patterns—Cisco’s Catalyst 9500 switches now auto-adjust QoS policies based on real-time application demands.

Leave a comment