HI, Greetings!
Today, I would like to explain the 5G mobile devices are currently widely available and in use by a large number of individuals. There are two different 5G network installations available when purchasing 5G mobile devices: NSA (Non-Standalone) and SA. (Standalone). Let’s get to the article now.
Intro
A new mobile network architecture called 5G SA (Standalone Architecture) does not rely on the 4G infrastructure already in place to enable communications. Instead, 5G standalone (SA) is a 5G implementation that relies entirely on a 5G core network for signaling and data transport, not on 4G LTE network control services. The radio access network and 5G infrastructure are used to build 5G SA networks. (RAN).
The 5G network is dependent on the current 4G LTE network infrastructure in 5G NSA (Non-Standalone Architecture), among other things, for call control and mobility management. This indicates that the 5G network is dependent on the 4G network and is unable to operate independently. While the standalone 5G infrastructure is being installed, the 5G NSA method is being employed as an early step to give 5G coverage.

SA 5G Architecture:
A 5G network design known as the SA (Standalone) 5G architecture does not rely on any 4G LTE or other previous-generation cellular network technologies. To put it another way, it is an entirely new architecture created especially for 5G networks.
Three crucial elements form the foundation of the SA 5G architecture:
1. User Equipment (UE):
This term describes 5G-capable gadgets including smartphones, tablets, and other Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
2. The 5G Core Network (Core):
Which connects the UE to other network services like data processing, storage, and security, is the foundation of the 5G network.
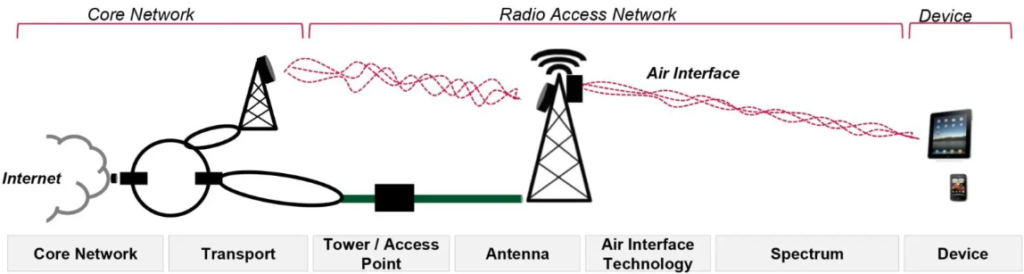
3. The 5G Radio Access Network (RAN):
The UE may access the internet wirelessly thanks to this network of cell towers and other infrastructure. (smartphone, tablet, etc.)
Compared to other cellular network generations, the SA 5G architecture offers more flexibility and adaptability. This is due to the fact that it is modular in design, allowing for the independent upgrade or replacement of individual components. It also makes it possible to use cutting-edge technologies like network slicing and edge computing, which can help deliver quicker and more effective network services.
NSA 5G Architecture:
A deployment strategy for 5G networks called NSA 5G (Non-Standalone 5G Architecture) integrates 5G technology with current 4G LTE networks. According to this architecture, 5G devices first connect to the 4G LTE network before switching to the 5G network for high-speed data transmission.
Since the NSA 5G architecture does not necessitate a total revamp of the current infrastructure, 5G networks may be deployed more quickly. Additionally, it makes it possible to use 5G services in places where standalone 5G networks might not be present or have not yet been fully implemented.
In this architecture, the 4G LTE core network, which manages operations like authentication, billing, and policy enforcement, is connected to the 5G radio access network (RAN). To interact with 5G user equipment (UE), such as smartphones and other devices, the 5G RAN is made up of 5G base stations, often referred to as gNBs (gNodeBs).
Overall, the NSA 5G architecture is a step-by-step strategy for deploying 5G that serves as a link between 4G and 5G networks and permits the ongoing use of existing infrastructure.
Advantages of SA 5G
• MNOs can introduce new 5G enterprise services like smart factories and cities.
• It has a cloud-native architecture (CNA) that is fully virtualized and brings new techniques for creating, deploying, and managing services.
• End-to-end slicing to conceptually distinct services is made possible by the architecture.
• Automation increases productivity while lowering network running costs.
• MNOs can rely on best-of-breed innovation from vendors and open-source communities by standardizing on a cloud-native strategy.
• MNOs can choose from several deployment strategies, including on-premises private cloud, public cloud, or hybrid, to achieve their business goals by selecting a cloud-native microservices-based architecture.
• On a SA 5G network, you receive extremely low and dependable latency that can reach as low as 5ms or less. This should be useful for streaming, cloud gaming, and other activities. Additionally, it can make remote robotic surgery possible in the medical area.
• In addition, SA 5G provides faster speed than NSA 5G. Theoretically, it is capable of 10–20 Gbps download speeds. So, the absurd boasts of being able to download a 1GB video in 5 seconds or so might come true.
• The SA 5G network can support over a million devices at once and can scale greatly.
• VoNR will improve your voice calling experience on a SA 5G network. (Voice over New Radio).
• The IEEE claims that SA 5G uses less power than NSA 5G and has many energy-saving features.
Advantages of NSA 5G
• Provide consumers with 5G-enabled gadgets with fast connectivity.
• Using current network investments in mobile core and transit. Because NSA 5G utilizes the current 4G core, it provides a quick and affordable solution for telecom operators to offer a 5G network.
• NSA 5G can provide voice conversations over LTE using the 4G core in the absence of VoNR.
• Although not even near SA 5G, an NSA 5G network has respectable download speeds, especially when compared to 4G/LTE. Impressive speeds of up to 1 Gbps are available.
• The 4G and 5G bands can simultaneously share their spectrums with DSS (Dynamic Spectrum Sharing) to provide a better experience.
What is the SA vs NSA 5G Difference?
The network architecture and deployment models of SA (Standalone) and NSA (Non-Standalone) 5G are the key differences between them.
Separate from the current 4G LTE network, SA 5G is a standalone architecture that uses an entirely new network infrastructure. As a result, SA 5G necessitates a comprehensive upgrade of the current infrastructure, which includes new 5G base stations, a 5G core network, and new user equipment (UE), such as 5G smartphones.
The NSA 5G rollout approach, on the other hand, combines 4G LTE infrastructure with 5G technology. The 4G LTE core network and the 5G radio access network (RAN) are linked in NSA 5G, enabling 5G devices to initially access the 4G network before switching to the 5G network for high-speed data transmission.
Higher bandwidth, lower latency, and the capacity to handle more connected devices are some of SA 5G’s primary advantages. This is so that more optimization and efficiency may be achieved, as the SA 5G architecture was created specifically for 5G technology. The drawback is that it necessitates a substantial investment in new infrastructure, which can be costly and time-consuming.
On the other side, NSA 5G provides a quicker and more affordable solution to deploy 5G networks. It keeps some advantages of 5G technology, such as greater data speeds and lower latency, while still allowing for the continuing use of existing infrastructure. NSA 5G might not be as scalable as SA 5G and might not be able to support all of the advanced capabilities of 5G.
The good news is that by the near future, every mobile network operator in the globe intends to deploy the real SA 5G core.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the network architecture and deployment models used by SA and NSA 5G differ significantly. While NSA 5G is a deployment strategy that incorporates 5G technology with current 4G LTE infrastructure, SA 5G is a standalone design that makes use of an entirely new network infrastructure.
SA 5G needs considerable investment in new infrastructure but delivers faster bandwidth, lower latency, and the capacity to handle more connected devices. However, it might not be able to handle all of the advanced capabilities of 5G and might not be as scalable as SA 5G. On the other hand, NSA 5G offers a quicker and more affordable approach to establishing 5G networks.
The decision between SA and NSA 5G will ultimately be based on several variables, including the availability of infrastructure, the desired degree of network performance, and the amount of investment that the network operator is willing to undertake. Both SA and NSA 5G have their benefits and drawbacks, and the network operator must decide which architecture best meets their requirements.
5G IS EMPOWERING THE FUTURE !!!
Thanks! Any ideas are welcome to leave a message. csd@telecomate.com





Leave a comment