Hello, everyone!
This post shares your knowledge about dispersion. I hope you like it!
Chromatic Dispersion (CD)
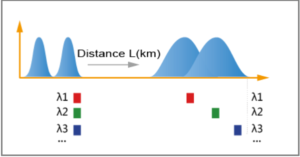
A form of dispersion where optical pulses are spread because different wavelengths are transmitted at different speeds in optical fibers and the periods for different wavelengths to traverse the same distance are different.
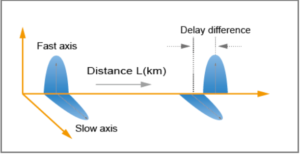
Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD)
A form of dispersion where optical pulsesare spread because optical signals in different phase status are transmitted at different speeds due to the random birefringence of optical fibers.
Impact of Dispersion on the System
The spreading of optical pulses in the time domain caused by CD and PMD will lead to distortion of signals and inter-code crosstalk, thereby causing bit errors.
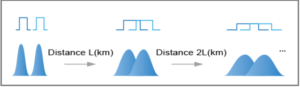
The dispersion is accumulated as the transmission distance is prolonged, and the impact of dispersion on the system also increases. As a result, the transmission distance is limited.
![]()
As the transmission speed increases, the pulse width is reduced, the impact of dispersion on the system becomes more serious.
Dispersion reduction technology
To avoid the impact of dispersion on communication, use optical modules with high dispersion tolerance and add dispersion compensation modules to the line.
Dispersion compensation fiber (DCF) is a mature technology to compensate the dispersion performance of transmission lines. The DCF is a special optical fiber. The chromatic dispersion of the DCF is negative, which is opposite to that of the G.652 optical fiber. The DCF can offset the impact of the conventional dispersion of the G.652 optical fiber on the line.
1. Dispersion tolerance and dispersion coefficient
The dispersion tolerance is defined as the maximum dispersion that the system can tolerate when the power penalty due to dispersion is 1 dB.
The dispersion coefficient is the difference between the arrival time of a 1-km optical fiber transmitted between two optical waves with a wavelength spacing of 1 nm. The unit is ps/nm·km.
2. Dispersion in G.652 and G.655
The typical dispersion coefficient of a G.652 single-mode long-wavelength fiber (SMF) is 17 ps/nm.km. In actual use, redundancy must be added. When the dispersion tolerance is converted to the dispersion-limited distance, the dispersion value of the fiber is 20 ps/nm.km.
The typical dispersion coefficient of a G.655 single-mode long-wavelength fiber is 4.5 ps/nm.km. In practice, the dispersion coefficient is 6 ps/nm.km.
3. For regular rate lines
Generally, the dispersion tolerance of a 2.5G line system is 12800 ps/nm. The distance is 12800/20 = 640 km. When the transmission distance is greater than 600 km, dispersion compensation needs to be considered.
For 10G lines and 40G non-coherent lines, the dispersion tolerance depends on the optical module model. If the dispersion tolerance of a 10 Gbit/s optical module is 1600 ps/nm, the distance is 1600/20 = 80 km. When the transmission distance is greater than 50 km, dispersion compensation needs to be considered.
4. For high-rate coherent lines
High-speed ADC and DSP algorithms are used to cancel the chromatic dispersion and PMD effect in the optical field. Therefore, dispersion compensation is not required in a coherent communication system. In Huawei WDM/OTN products, the coherent communication technology is used for large-bandwidth transmission. (Some 40G line rates, all 100G line rates, and above 100G line rates).
Thank you!

Leave a comment